Organization of ITI’s and Scope of the Electrician Trade
Learning Objectives
- At the end of this lesson, you shall be able to provide a brief introduction about Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs).
- You will be able to explain the organized structure of the Institute.
- You will understand the scope and career pathways in the Electrician Trade.
About Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs)
Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs) play a vital role in strengthening the country’s economy by producing skilled manpower. These institutes function under the Directorate General of Training (DGT), which operates under the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE).
Key highlights:
- All vocational training programs are conducted under the National Council of Vocational Training (NCVT).
- NCVT implements two major programs:
- Craftsmen Training Scheme (CTS)
- Apprenticeship Training Scheme (ATS)
- After completing training and passing the All India Trade Test (AITT), trainees receive a National Trade Certificate (NTC), which is recognized internationally.
- With an NTC, trainees can undergo Apprenticeship Training (ATS) for one or two years to earn a National Apprenticeship Certificate (NAC).
Organizational Structure of an ITI
The organizational structure of an ITI ensures smooth training and administrative operations.
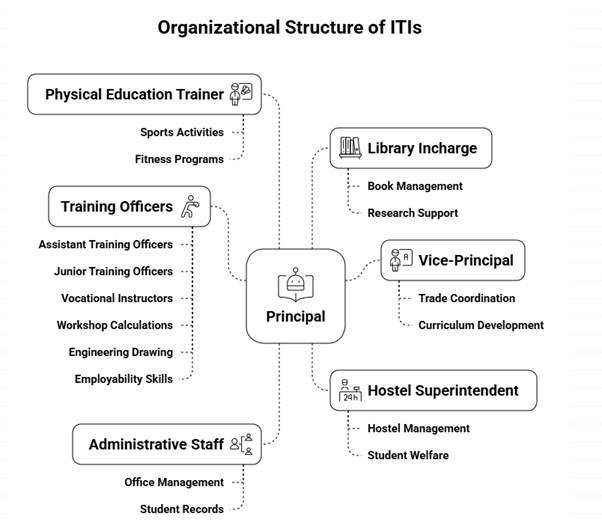
- Principal – Head of the Institution.
- Vice Principal (VP) – Assists the Principal in managing operations.
- Training Officers (TO) / Group Instructors (GI) – Handle supervision and training management.
- Assistant Training Officers (ATO), Junior Training Officers (JTO), Vocational Instructors (VI) – Provide trade-specific training under TO/GI guidance.
- Administrative Staff – Includes Hostel Superintendent, Librarian, and support staff.
Scope of the Electrician Trade
The Electrician trade under CTS is one of the most sought-after vocational courses with a duration of two years. It is classified under the National Code of Occupation (NCO) as:
- Electrician General (NCO Code: 7411.0100)
- Electrical Fitter (NCO Code: 7412.0200)
Duties of Electrician General and Electrical Fitter
Electrician General
- Installs, maintains, and repairs electrical machinery and fittings.
- Studies drawings to understand circuit layouts and installs equipment such as motors and transformers.
- Tests installations and locates faults using tools like meggers or test lamps.
Electrical Fitter
- Fits and assembles electrical machinery such as motors, transformers, and switch gears.
- Erects equipment like bus bars, panel boards, and fuse boxes based on technical drawings.
- Checks for continuity, resistance, and short circuits using various testing appliances.
Career Pathways and Job Opportunities
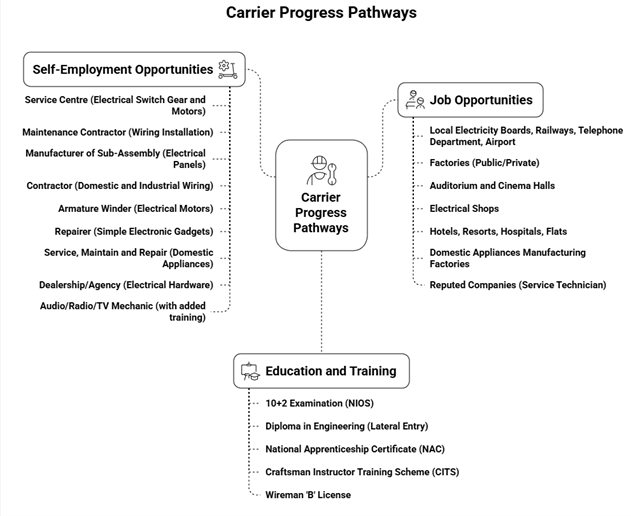
Career Pathways
- After ITI, trainees can appear for the 10+2 exam via NIOS (National Institute of Open Schooling).
- They may gain lateral entry into engineering diploma courses.
- They can join the Craftsman Instructor Training Scheme (CITS) to become ITI instructors.
Job Opportunities
- Employment in government organizations such as electricity boards, railways, and airports.
- Roles include assembler of control gears, winder of electrical motors, and technician roles in power and manufacturing industries.
Self-Employment Opportunities
- Starting a service center for repairing motors, transformers, and switch gears.
- Working as a contractor for domestic and industrial wiring projects.
Conclusion
The Electrician Trade offers promising career opportunities in both government and private sectors, along with scope for entrepreneurship. ITIs, with their structured training programs, play a vital role in equipping students with the skills necessary to meet industrial demands and build sustainable careers.
