Basic Electrical Practice: A Complete Guide for ITI Electrician Module-4
Understanding Basic Electrical Practice is essential for every aspiring electrician. This module covers crucial topics like Ohm’s Law, Kirchhoff’s Laws, DC circuit analysis, resistance behavior, and electromagnetism. These concepts form the foundation of electrical engineering and practical work in any electrical field.
Ohm’s Law in Basic Electrical Practice
Learn how Ohm’s Law applies to basic electrical practice through real circuit examples and exercises.
Ohm’s Law states that the current flowing through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points. It is mathematically represented as:

V = I × R
Where:
V = Voltage (Volts)
I = Current (Amperes)
R = Resistance (Ohms)
Practical Circuit Example:
If a 12V battery is connected to a resistor of 4 ohms, the current is:
I = V/R = 12/4 = 3A
Learning Outcome:
- Ability to calculate voltage, current, and resistance in simple circuits.
- Solve basic Ohm’s Law problems in real-world scenarios.
Applying Kirchhoff’s Law in Electrical Practice
Explore Kirchhoff’s Laws with real-world applications in basic electrical circuits.
Kirchhoff’s Laws are critical in understanding current and voltage distribution in electrical networks.
Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL):
The total current entering a junction is equal to the total current leaving the junction.
Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL):
The sum of all voltages around a closed loop is zero.
Application:
Used to solve complex circuit networks with multiple loops and junctions.
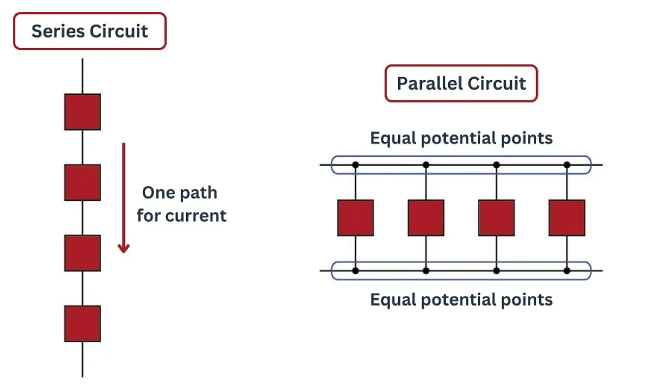
DC Series and Parallel Circuits in Basic Electrical Practice
Understand series and parallel DC circuits essential in foundational electrical practice.
Series Circuit:
- Current is the same through all components.
- Total resistance = R₁ + R₂ + R₃…
Parallel Circuit:
- Voltage is the same across all branches.
- 1/RT = 1/R₁ + 1/R₂ + 1/R₃…
Skill Gained:
- Calculate total resistance, voltage drops, and current in DC circuits.
Troubleshooting Open and Short Circuits in Electrical Practice
Identify and fix circuit issues as part of essential basic electrical skills.
Open Circuit:
- No current flows; it behaves like an infinite resistance.
- Troubleshooting tip: Check for loose or broken connections.
Short Circuit:
- Direct connection with zero resistance.
- Causes high current flow; can damage components.
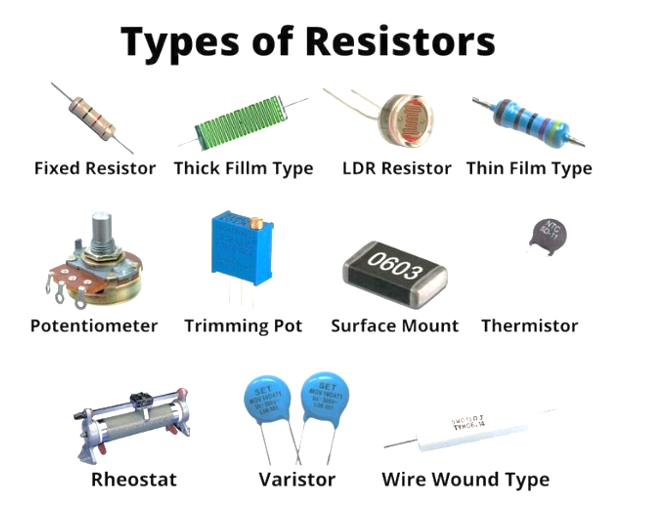
Types of Resistors and Resistance Laws in Electrical Circuits
Study resistance behavior and resistor types, crucial in basic electrical circuits.
Laws of Resistance:
Resistance depends on:
- Material of the conductor
- Length of the conductor
- Cross-sectional area
- Temperature
Formula:
R = ρ × (L/A)
Types of Resistors:
- Fixed Resistors (Carbon, Wire-wound)
- Variable Resistors (Potentiometers)
- Special Resistors (Thermistors, LDRs)
Wheatstone Bridge Applications in Basic Electrical Practice
Learn how to use a Wheatstone Bridge for accurate resistance measurement.
The Wheatstone Bridge is a circuit used to measure unknown resistance using a balanced condition.
Principle:
When the bridge is balanced: (R1/R2) = (R3/Rx)
Applications:
- Precision resistance measurement
- Sensor circuits in industries
Effect of Temperature on Resistance in Electrical Circuits
Analyze how temperature variations affect resistors in electrical systems.
Effect:
- Metals: Resistance increases with temperature.
- Semiconductors: Resistance decreases with temperature.
Real-world Relevance:
Understanding this helps in choosing materials for specific environments.
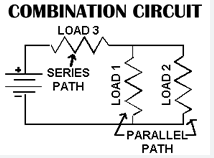
Combination Circuits in Basic Electrical Practice
Explore circuits combining series and parallel elements in real applications.
Example:
A resistor R1 is in series with a parallel combination of R2 and R3.
Calculation Steps:
- Find the equivalent of R2 and R3.
- Add R1 to the result.
Magnetic Materials and Terms in Electrical Practice
Discover magnetic properties and materials used in foundational electrical setups.
Magnetic Terms:
- Magnetic Flux (Φ)
- Magnetic Field (B)
- Permeability (μ)
Magnetic Materials:
- Soft Iron (high permeability, easily magnetized)
- Steel (retains magnetism)
Properties of a Magnet:
- Attraction
- Repulsion
- Magnetic field lines
- Poles
Laws of Electromagnetism in Basic Electrical Practice
Understand electromagnetic theory and its application in basic electrical training.
Electromagnetic Principles:
- Current-carrying conductors produce a magnetic field.
- Right-hand rule and left-hand rule determine direction of field and force.
Important Laws:
- Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction
- Lenz’s Law
Applications:
- Electric motors
- Transformers
- Inductors
Conclusion: Why Mastering Basic Electrical Practice Is Crucial
The Basic Electrical Practice module gives you the foundation to move forward in the electrical trade with confidence. Mastering the laws of electricity, understanding circuits, analyzing resistors, and applying electromagnetism are essential skills for any ITI Electrician student.
Whether you’re preparing for exams or real-world applications, this guide offers a solid starting point.
